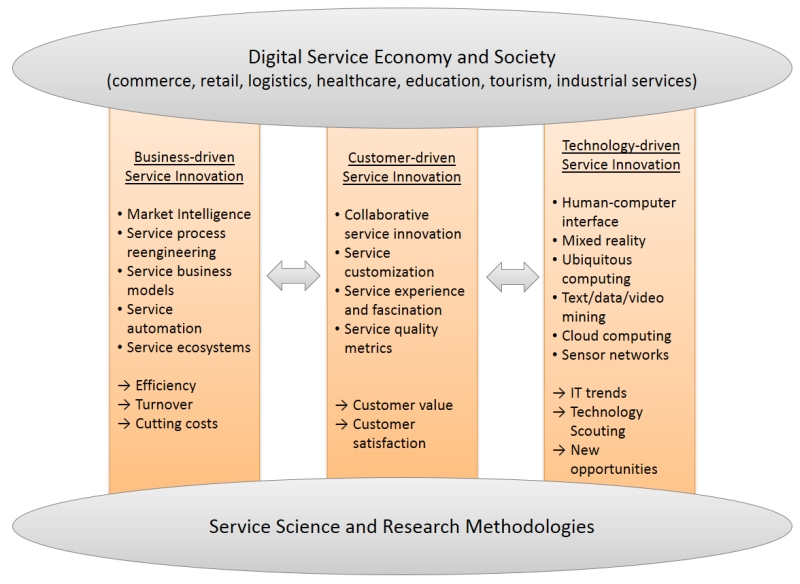
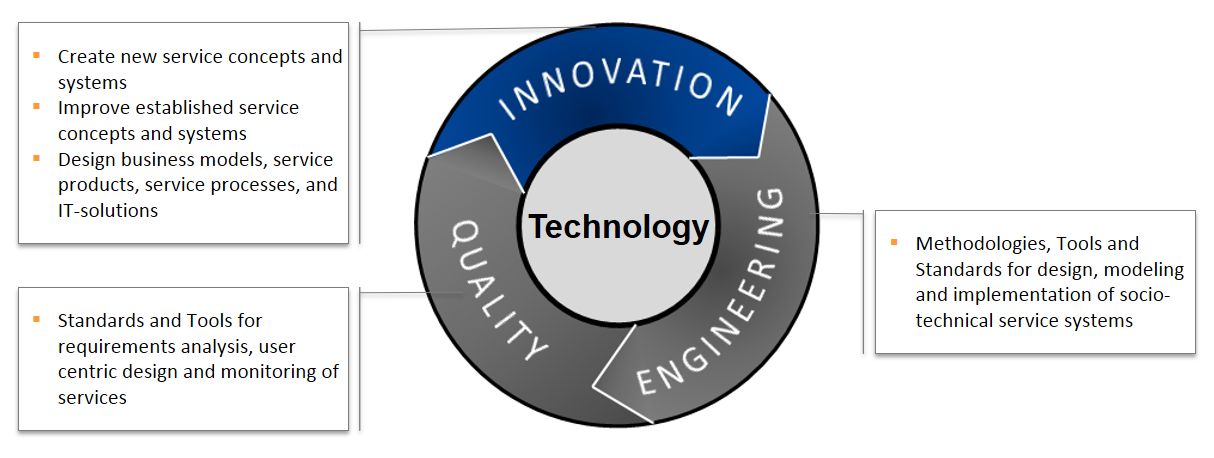
Service science is a multidisciplinary discipline based on fundamental science and engineering theories, models, and applications, aiming at enhancing and improving service innovation. Our view of service innovation focuses on three key drivers: business, customer, and technology.
For the creation of service innovations there are two generic approaches. On the one hand screening new technologies can be used to develop new service opportunities. On the other hand customer relationships can be investigated to shape innovative services. Screening technical possibilities is necessary to answer the question “What can we do and how?”.
The complementary question to create successful service innovations is “What should we do?”. This question is answered by investigating customer needs and requests. This can be seen as customer-pulled service innovation. In addition there is a third approach revealing innovation needs coming from the business perspective and the service company itself. Business-invented service innovations are serving the needs of entities inside the company and strive for increasing profitability, reducing costs, etc.
Analyzing the answers results in the challenge “What will we do?” and in the combination of services science research with business development through the application of technology. This follows a lifecycle approach with Innovation – Engineering – Quality Assurance as the main stages.
In many domains services are crucial to gain competitive advantage. Besides traditional service industries, originally manufacturing-oriented companies are redefining their strategy to a solution-based service organization. Most of these organizations are shifting from a product-dominant logic to a service-dominant logic, focusing on enhanced product-related services (hybrid products – product-service bundles) to improve the end-user experience.
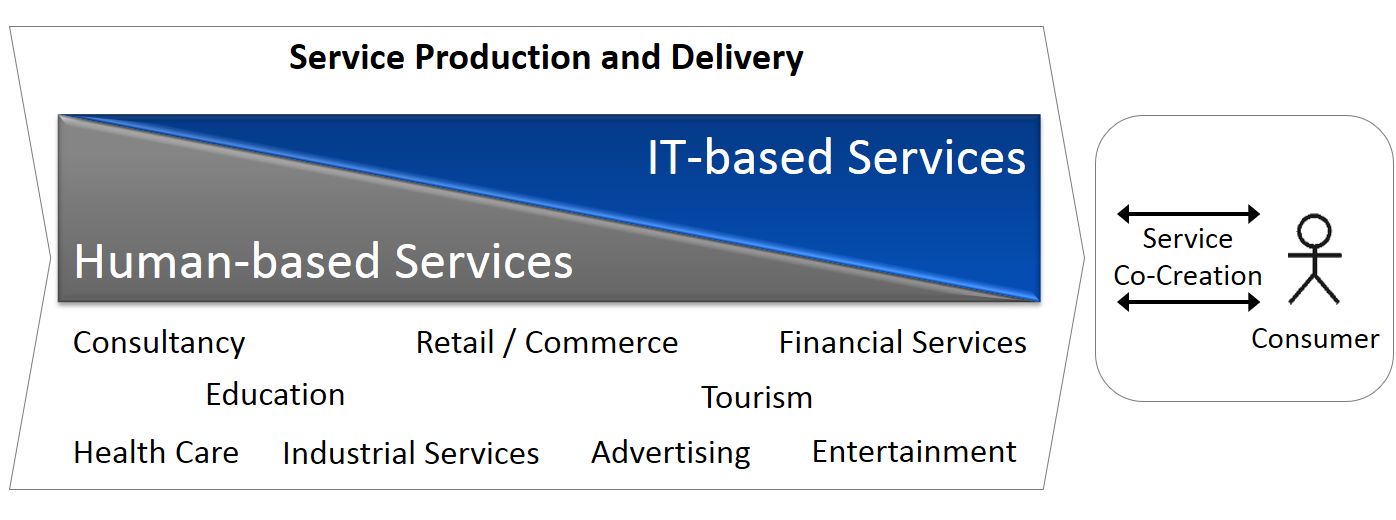
Today, a shift from people-based services towards IT-based services is unveiled. There are services that have been deploying primarily personnel for service production and delivery in the past and still depend on these human resources. On the other hand, services traditionally based on personnel may now rely almost completely on information technology. For example, taking a look into the health care sector reveals that this service industry still is primarily based on personal producer-consumer interaction. But physicians capitalize more and more on information technology supporting their work.
Retail and education provide examples where IT-based services are emerging in parallel to people-based services, leading to the point that one might substitute the other. E. g., e-commerce substitutes existing retail stores, offering products on the internet for sales. The same is true for trainings which historically have been performed by an instructor in front of participants in a class room. Nowadays, e-learning enables to teach and train by IT systems.
Examples in the field of advertising demonstrate another category where IT paves completely new ways to provide services. Whereas advertising was formerly based on traditional media like newspapers, television, or advertising pillars in the streets, the internet and new technologies like virtual reality open the door to a completely new world of services.
To sum up, the mission of the Competence Center Services is to foster IT-based service innovations that improve and enhance existing services as well as create new services by applying cutting-edge technologies and IT systems.